LayoutManger使用
LayoutManager 是配合 RecyclerView 使用的,它主要的作用是控制 RecyclerView 子item的显示布局。比如自带的实现有:
- LinearLayoutManager。支持X轴线性布局或者Y轴线性布局
- GridLayoutManager。网格布局
- StaggeredGridLayoutManager。流式布局。
使用起来也是非常的简单:
1
recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager()
设计成插拔式,将数据与布局完美的拆分开来,可以说是非常流弊了。
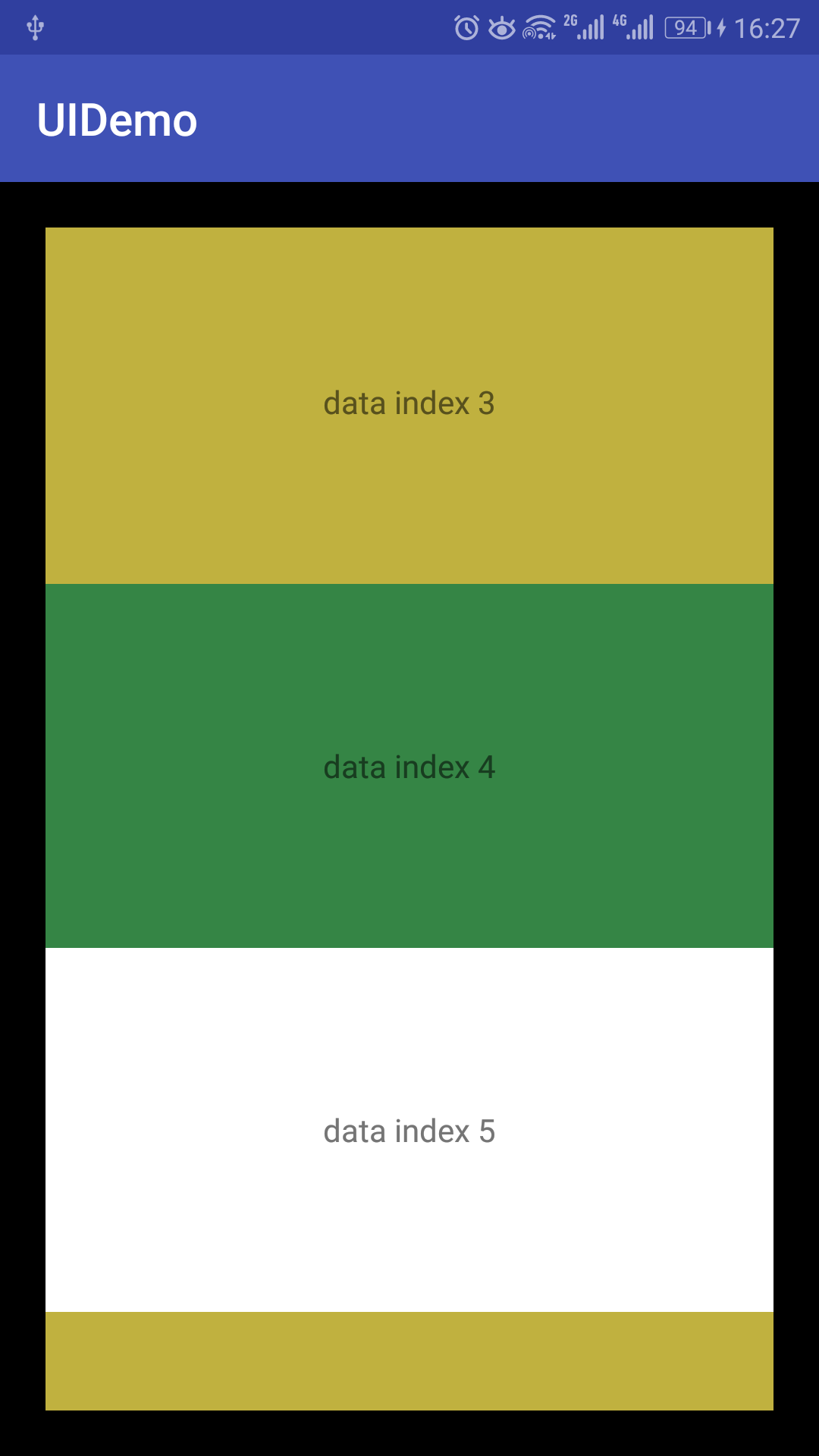
自定义LayoutManager,实现简单的垂直布局
LayoutManager 是 RecyclerView 的静态内部抽象类,自定义LayoutManager需要继承它,并要复写其中的几个方法:
- generateDefaultLayoutParams()。 设置默认的布局参数,主要是给子item使用的。
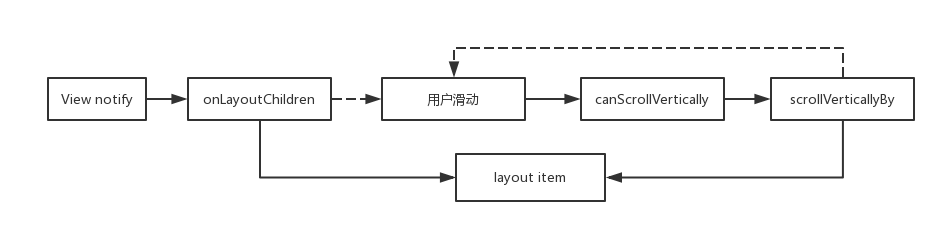
- onLayoutChildren()。布局子item,当recyclerView调用notify的时候,会调用该方法。
- canScrollVertically()。 能否垂直滚动。因为是垂直布局,所以要复写该方法。
- scrollVerticallyBy()。垂直方向滚动的距离(与上一个位置的距离差), 需要在这里面重新布局界面。
调用流程如下:
效果图:
完整代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
import android.graphics.Rect
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
import android.util.Log
class DemoLayoutManager : RecyclerView.LayoutManager() {
val TAG = javaClass.simpleName
//滑动的总距离
var mScrollOffset = 0
//item高度和
var totalHeight = 0
var allItemRects = mutableMapOf<Int, Rect>()
override fun generateDefaultLayoutParams(): RecyclerView.LayoutParams {
return RecyclerView.LayoutParams(RecyclerView.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
RecyclerView.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)
}
override fun onLayoutChildren(recycler: RecyclerView.Recycler, state: RecyclerView.State) {
if (itemCount == 0 || state.isPreLayout) {
return
}
//layout item之前,需要detach所有的view
detachAndScrapAttachedViews(recycler)
//计算item总高度
(0 until itemCount).map { recycler.getViewForPosition(it) }
.forEachIndexed { index, indexedValue ->
measureChildWithMargins(indexedValue, 0, 0)
val width = getDecoratedMeasuredWidth(indexedValue)
val height = (width * 0.5F).toInt()
allItemRects[index] = Rect(0, totalHeight, width, totalHeight + height)
Log.d(TAG, allItemRects[index].toString())
totalHeight += height
}
//layout item
doLayout(recycler, state)
}
private fun doLayout(recycler: RecyclerView.Recycler, state: RecyclerView.State) {
val displayRect = Rect(0, mScrollOffset, width, height + mScrollOffset)
(0 until itemCount).filter { Rect.intersects(displayRect, allItemRects[it]) }
.forEach {
val view = recycler.getViewForPosition(it)
measureChildWithMargins(view, 0, 0)
addView(view)
//在手动measure完view的大小之后,需要调用 calculateItemDecorationsForChild ,计算出item decorator的大小,并保存在lp.mDecorInsets中
//因为后续需要用到这个值, layoutDecorated 方法便需要用到
calculateItemDecorationsForChild(view, Rect())
val rect: Rect = allItemRects[it]!!
layoutDecoratedWithMargins(view, rect.left, rect.top - mScrollOffset, rect.right,rect.bottom - mScrollOffset)
}
}
override fun canScrollVertically(): Boolean {
return true
}
override fun scrollVerticallyBy(dy: Int, recycler: RecyclerView.Recycler, state: RecyclerView.State): Int {
//layout item之前,需要detach所有的view
detachAndScrapAttachedViews(recycler)
val preScrollOffset = mScrollOffset
mScrollOffset = Math.min(Math.max(0, mScrollOffset + dy), totalHeight - height)
offsetChildrenVertical(preScrollOffset - mScrollOffset)
//layout item
doLayout(recycler, state)
return mScrollOffset - preScrollOffset
}
}
卡牌叠加式布局实现
效果图:
实现思路:
每个item在屏幕中自下而上显示,周期 与 item从底部显示开始滑动长度为 totalItemInScreen * itemHeight相同。
而item开始scale的点是在scrollOffset滑动了itemHeight长度之后。
那item在屏幕中显示的scale与top,便可以与scrollOffset这个变量之间,存在关系了。
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
import android.graphics.Rect
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
import android.util.Log
class Demo2LayoutManager : RecyclerView.LayoutManager() {
val TAG = javaClass.simpleName
var mScrollOffset = 0 //滑动总长度
var itemWidth = 0
var itemHeight = 0
val totalItemInScreen = 7 //一个屏幕中item的个数
val minItemScaled = 0.7F //item最多可以scale的大小
override fun generateDefaultLayoutParams(): RecyclerView.LayoutParams {
Log.d(TAG, "generateDefaultLayoutParams")
return RecyclerView.LayoutParams(RecyclerView.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
RecyclerView.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)
}
override fun onLayoutChildren(recycler: RecyclerView.Recycler, state: RecyclerView.State) {
Log.d(TAG, "onLayoutChildren")
if (itemCount == 0 || state.isPreLayout) {
return
}
detachAndScrapAttachedViews(recycler)
itemWidth = (width * 0.9F).toInt()
itemHeight = (itemWidth * 1.6F).toInt()
doLayout(recycler, state)
}
private fun doLayout(recycler: RecyclerView.Recycler, state: RecyclerView.State) {
val bottomVisiblePosition = Math.ceil(mScrollOffset / itemHeight.toDouble()).toInt()
val bottomViewHeight = if (mScrollOffset % itemHeight == 0) itemHeight else mScrollOffset % itemHeight
val viewLayoutInfoList = mutableListOf<ViewLayoutInfo>()
viewLayoutInfoList.add(ViewLayoutInfo(bottomVisiblePosition, 1.0F, getRecyclerViewHeight() - bottomViewHeight))
if (bottomVisiblePosition > 0) {
IntRange(0, bottomVisiblePosition - 1).reversed().forEach {
val offset = (bottomVisiblePosition - 1 - it) * itemHeight + bottomViewHeight
val rate = 1 - offset / (itemHeight * (totalItemInScreen - 1F))
val scale = (1 - minItemScaled) * rate + minItemScaled
val top = (getRecyclerViewHeight() - itemHeight) * rate * rate
viewLayoutInfoList.add(ViewLayoutInfo(it, scale, top.toInt()))
if (rate <= 0F) return@forEach
}
}
viewLayoutInfoList.forEach {
val view = recycler.getViewForPosition(it.position)
measureChildWithMargins(view, 0, 0)
addView(view, 0)
calculateItemDecorationsForChild(view, Rect())
val left = (getRecyclerViewWidth() / 2 - itemWidth * it.scale / 2).toInt()
val right = (left + itemWidth * it.scale).toInt()
val top = it.top
val bottom = (top + itemHeight * it.scale).toInt()
layoutDecoratedWithMargins(view, left, top, right, bottom)
}
}
override fun canScrollVertically(): Boolean {
Log.d(TAG, "canScrollVertically")
return true
}
override fun scrollVerticallyBy(dy: Int, recycler: RecyclerView.Recycler, state: RecyclerView.State): Int {
Log.d(TAG, "scrollVerticallyBy")
detachAndScrapAttachedViews(recycler)
val preScrollOffset = mScrollOffset
mScrollOffset = Math.min(Math.max(0, mScrollOffset + dy), itemHeight * (itemCount - 1))
offsetChildrenVertical(preScrollOffset - mScrollOffset)
doLayout(recycler, state)
return mScrollOffset - preScrollOffset
}
private fun getRecyclerViewWidth() = width
private fun getRecyclerViewHeight() = height
}
ViewLayoutInfo 结构如下:
1
2
3
data class ViewLayoutInfo(var position: Int, //item position
var scale: Float, //item scale的大小
var top: Int) //item top的y轴坐标